Advanced software that scans billions of web pages, images, and documents on the internet and ranks the most relevant results to the user’s keywords within seconds is called a search engine. These systems act like a compass that prevents you from getting lost in the endless ocean of information in the digital world, and they serve as a technological bridge that helps you reach the information, product, or service you are looking for in the shortest way possible.
Working in the background with highly complex algorithms, these mechanisms analyze, classify, and store content in their massive databases thanks to bots that regularly visit websites. When you submit a query, the system instantly searches this enormous index and, by considering hundreds of different criteria, brings the source that best meets your need to the top of the results.
Having become an indispensable part of daily life, these technologies make internet use practical by transforming scattered data into meaningful and accessible information. Beyond being merely a tool for finding information, they make the functioning of the web ecosystem possible by enabling users to solve problems, discover new things, and interact with entities in the digital world.
What Do Search Engines Do?
The most fundamental benefit search engines provide is helping users reach the right source without getting lost among vast piles of information in the digital world. These systems save time by filtering complex and disorganized internet data within seconds and make the web experience far more efficient. Beyond being simple query tools, they function like intelligent assistants that organize daily life, accelerate decision-making processes, and remove technical barriers to accessing information.
The main use cases and functions of these platforms—which add value by making sense of users’ movements on the internet—are as follows:
- Fast Access to Information: From academic research to everyday curiosities, they instantly analyze data and present the most accurate answer.
- Navigation and Local Discovery: Through map integrations, they make it possible to find the nearest restaurant, on-duty pharmacy, or the best route to take.
- Shopping and Comparison: By listing prices, features, and user reviews of searched products on a single screen, they make purchasing decisions easier.
- Following the Agenda: By bringing breaking developments in the world and locally to the user in real time, they speed up the process of getting news.
- Finding Multimedia Content: Not only text, but also direct access to content in different formats such as video, images, and audio files.
The functionality provided by these technologies transforms the internet from a static data repository into a living, dynamic, and interactive platform. Thanks to advanced algorithms that place user experience at the center, reaching the most satisfying result—whatever the search intent may be—has evolved into an effortless process. As a result, the practical solutions offered by these systems lie at the foundation of modern digital literacy and a data-driven way of life.
Most Popular Search Engines
Although there is intense competition among the tools we use to access information in the digital world, the real dominance of the market remains in the hands of a few major giants. Serving billions of users globally, these systems stand out from competitors thanks to advanced infrastructures and additional features that improve the user experience. Some services deliver excellent solutions for regional needs, while others stand out with universal-scale data processing capacity. Today, the most frequently preferred and proven reliable services include the following:
- Google: The undisputed market leader that single-handedly accounts for a very large portion of internet searches. With advanced AI support, a massive database, and integration with other digital services, it delivers the most relevant results at the highest speed.
- Bing: Developed by Microsoft, this platform stands out especially for its visual search capabilities and video preview features. Its full compatibility with the Windows operating system and its rewards programs have helped it build a significant user base.
- Yandex: Although based in Russia, it is also quite popular in the Turkish market. Its success in maps and navigation services, along with its clear strength in visual search technology, makes it a strong alternative.
- Yahoo: A long-established service that has been around since the early days of the internet. In addition to its search function, it continues to be used by a loyal audience thanks to its integrated structure with news, email, and finance services.
- DuckDuckGo: Built with a strong focus on user privacy above all else. Because it does not collect personal data, does not track users, and does not store search history, it is the number one choice for those who prioritize digital security.
When making a choice, determining which platform best meets your needs directly affects your internet experience. For some users, personalized results and speed are the priority, while for others, remaining anonymous or accessing regional data may be far more valuable. Trying different services makes it easier to reach the most accurate source depending on the type of information you are seeking and increases your mobility in the digital world.
The History of Search Engines
In the early years of the internet, accessing information was not as effortless as it is today; users relied on manual lists or simple directories to find websites. The need to bring order to this digital chaos led to the emergence of pioneering software that laid the groundwork for the massive algorithms we use today. From basic FTP archives to AI-supported ecosystems, this journey is filled with turning points that prove how quickly technology has evolved.
The key milestones that shaped the industry’s development and changed our digital habits are as follows:
- Archie (1990): Considered the ancestor of search engines, this system made it possible to find downloadable files by indexing filenames on FTP servers rather than searching content.
- Yahoo! (1994): Initially launched as “Jerry and David’s Guide to the World Wide Web,” it gained huge popularity with a manual directory approach that categorized websites.
- AltaVista (1995): One of the first advanced systems able to offer extensive bandwidth and process natural-language queries, and the strongest player of the pre-Google era.
- Google (1998): With the revolutionary PageRank algorithm that analyzes page links, it raised relevance to a unique level and seized leadership in the industry.
- The Modern Era and Artificial Intelligence: After 2010, algorithms moved beyond keyword matching into an intelligent era focused on understanding user intent and semantic context.
This rapid transformation from past to present shows that search technologies have evolved from being mere ranking tools into personal assistants that make life easier. As user expectations rise, these systems continue to develop through voice commands, visual scanning, and predictive results. In the future, it is entirely possible that we will encounter far more proactive structures that know what we need before we even ask.
How Do Search Engine Bots (Crawlers/Spiders) Work?
Acting as the unseen workers of the internet, these advanced programs are responsible for continuously visiting billions of pages across the web to discover new or updated content. The crawling process typically starts from previously known high-authority addresses and follows links on pages, tracing a route that expands like a network. These digital explorers work like meticulous librarians organizing shelves in a vast library, carefully examining every piece of text, image, and code structure they encounter.
Discovered data is not left in raw form; after being transmitted to servers, it goes through a complex process of analysis and interpretation. The software reads a page’s HTML code to evaluate the topic, keyword density, and technical health. The information is then categorized and stored in massive databases, while critical signals such as originality and the value offered to users are recorded. The core purpose is to build an organized archive that can deliver the most accurate result within milliseconds when a search is performed.
This operation is not a one-time action; systems revisit websites at regular intervals to check for changes. A website’s publishing frequency, technical performance, and popularity are the main factors that determine how often bots will return. In a digital ecosystem that is constantly alive and evolving, keeping search results up to date is made possible by this continuous cycle.
Average Usage Rates of Search Engines
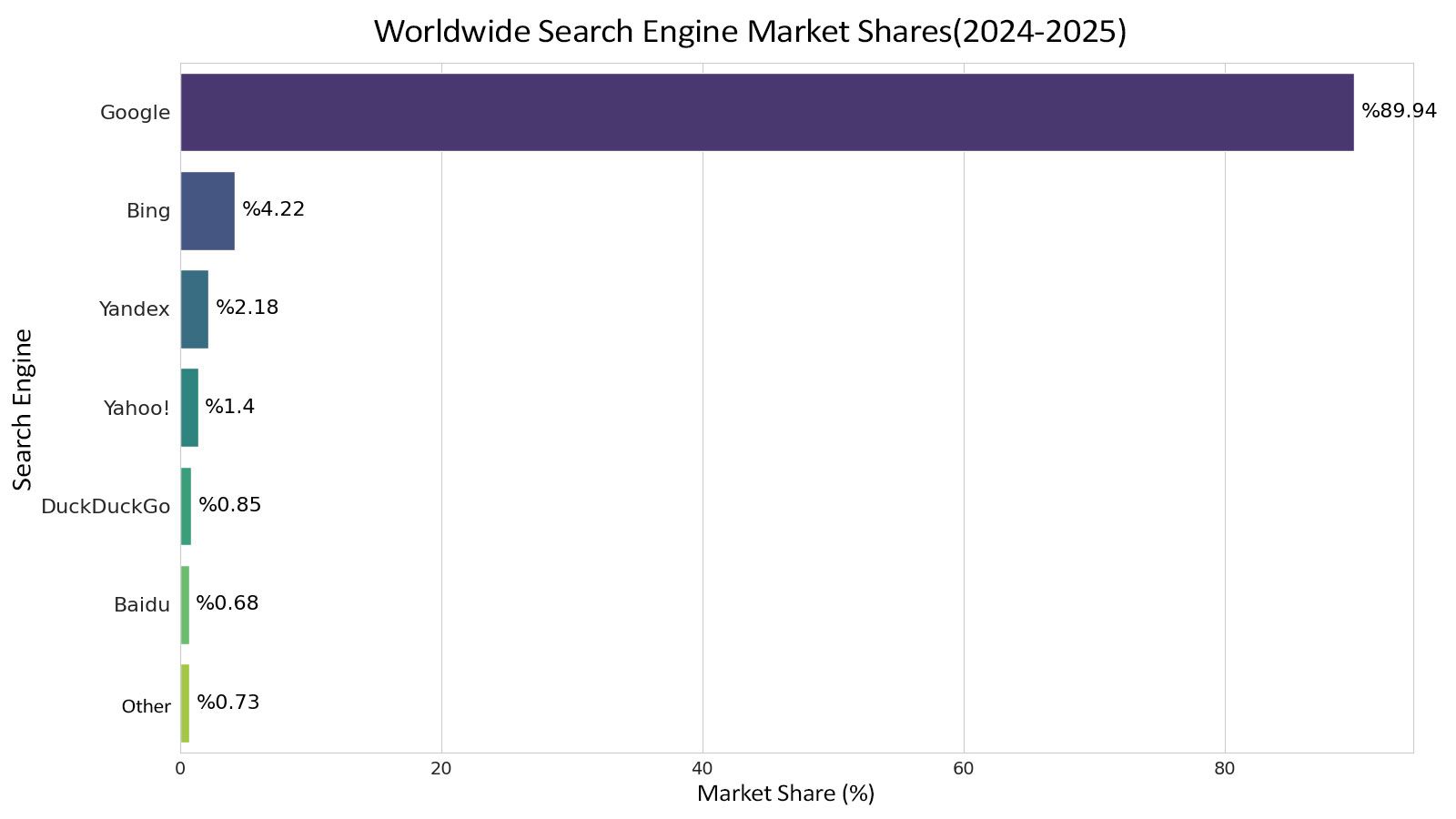
When looking at the global digital market, one name’s overwhelming dominance in search engine usage rates stands out clearly. Google has maintained its leadership for years, remaining the undisputed ruler of the sector with a market share approaching 90%. This massive figure demonstrates that the primary preference of billions of users for accessing information has not changed, highlighting how deeply rooted these habits are. Especially on mobile devices, built-in usage and the widespread reach of the Android ecosystem are among the biggest factors behind this persistently high and resilient statistic.
The remaining small slice of the market is shared among alternative platforms and regional players. Microsoft-backed Bing holds a global usage rate that generally ranges between 3% and 4%, although in some corporate markets and desktop usage this rate can increase noticeably. Meanwhile, local giants such as Yandex and Baidu have reach far beyond global averages within their own geographies. Particularly in regions like Russia and China, where local dynamics and language factors are dominant, these services can reach levels that allow them to compete head-to-head with global giants.
When recent user trends are examined, a notable shift toward privacy-focused search engines and next-generation tools with AI integration can be observed. Platforms like DuckDuckGo, which do not track personal data, still hold a small share of the overall pie, but they show steady growth by building a loyal audience. Growing sensitivity around data security and the increasing prevalence of AI-powered answers indicate that major changes may occur in the coming years in these seemingly stable usage statistics.
























Do Comment